分治法-快速排序
算法思想:分治法
实际问题:快速排序
编写语言:Java
Java代码
//本篇博文代码主要有两种基准选择方式:基准=低下标处的值,基准=随机值
import java.util.Random;
public class QuickSort
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] ary = new int[] {1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 7, 0, 6, 9, 8};
System.out.print("排序前的数组:");
for(int i = 0; i < ary.length; i++)
System.out.print(ary[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
sort(ary);
System.out.print("排序后的数组:");
for(int i = 0; i < ary.length; i++)
System.out.print(ary[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void sort(int[] a)
{
sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
public static void sort(int[] a, int low, int high)
{
//当low == high时就返回
//确保数组元素为1时就停止划分,防止数组下标越界
if(low < high)
{
int pivot = randPart(a, low, high);
sort(a, low, pivot - 1);
sort(a, pivot + 1, high);
}
}
//划分寻找基准
public static int part(int[] a, int low, int high)
{
int pivot = a[low];
while(low < high)
{
//1、从右往左找比基准小的数
while(low < high && a[high] > pivot)
high--;
//a处赋值
if(low < high)
a[low] = a[high]; //此时是 a[high] < pivot, a[low] < pivot
//2、从左往右找比基准大的数
while(low < high && a[low] <= pivot)
low++;
//3、一次寻找结束,交换两个值
//b处赋值
if(low < high)
a[high] = a[low]; //此时是 a[high] > pivot, a[low] < pivot
//a、b两处赋值,相当于一次交换,只是分开了
}
//将pivot放到left和right相遇的地方
a[high] = pivot;
return high;
}
//划分寻找基准-随机化优化
public static int randPart(int[] a, int low, int high)
{
Random r = new Random();
//随机产生一个 low 到 high 的整数
int flag = low + r.nextInt(high - low + 1);
int pivot = a[flag];
//此处交换保证 1 处的赋值不出错,
//因为只要原 a[low] < pivot,那么这个交换算法就失败了
a[flag] = a[low];
a[low] = pivot;
while(low < high)
{
//1、从右往左找比基准小的数
while(low < high && a[high] > pivot)
high--;
if(low < high)
a[low] = a[high];
//2、从左往右找比基准大的数
while(low < high && a[low] <= pivot)
low++;
if(low < high)
a[high] = a[low];
}
//将pivot放到low和high相遇的地方
a[high] = pivot;
return high;
}
}
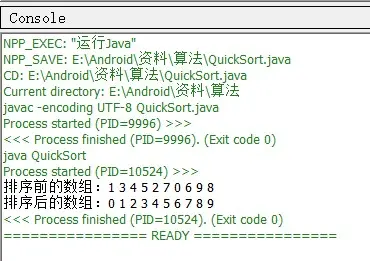
运行结果